Contents
- Index
Ppk
Capability index that measure the relative distance to the nearest spec limit:
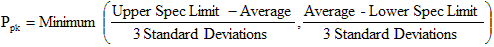
The numerator is the distance to the nearest spec limit. For a one-sided spec limit (lower spec only or upper spec only) only use the portion of the formula for that spec limit. The denominator is 3 standard deviations, which can be thought of as the half the width of the process. For the normal distribution 99.7% of values fall within +/-3 standard deviations of the average or into an interval 6 standard deviations wide. A Ppk value of 1 means the distance between the average and the nearest spec limit is 3 standard deviations and thus the process fills this interval and touches the spec limit. A Ppk value of 2 means the distance between the average and the nearest spec limit is 6 standard deviations and thus the process fills only half this interval. This leaves a safety margin. The larger Ppk is, the better the capability.
Ppk is similar to the capability index Cpk. They are both calculated using the formula above. However, they use different methods for estimating the standard deviation. Ppk uses the total standard deviation. Cpk requires that the units be collected in subgroups over time and uses the within subgroup standard deviation, ignoring the effects of shifts between subgroups. Ppk estimates actual performance, while Cpk estimates the capability the process could achieve if made stable over time.
The acceptance criteria for a variable sampling plan can be stated in terms of the capability indexes Pp and Ppk.
Note: Ppk depends on both the average and standard deviation. Further Ppk can be calculated when there is any combination of spec limits: lower only, upper only and both upper and lower spec limits.